Memory Storage
Next Lesson
Summary
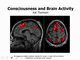
The content delves into the intricacies of Memory Storage, exploring the transition of information through sensory, short-term, and long-term memory stages, and the mechanisms that underpin these processes.
- There are three kinds of memory storage: sensory, short-term, and long-term, with sensory memories lasting about one to two seconds, providing continuity to our experiences.
- Short-term memory, or working memory, has a duration of 15 to 30 seconds and is crucial for temporary information storage, with a capacity of 4 to 9 items.
- Long-term memories can last indefinitely and are formed through various kinds of rehearsal from short-term memories, involving processes in the hippocampus and neocortex.
- Broadbent's Filter theory and the concept of selective attention play significant roles in determining which sensory inputs transition into short-term and then long-term memories.
- Emotional memories, particularly those involving fear, can form in parallel rather than sequentially, highlighting the amygdala's role in memory formation.
Chapters
00:00
Introduction to Memory Storage
00:37
The Three Kinds of Memory Storage
04:29
Short-Term to Long-Term Memory Transition
05:17
Selective Attention and Memory Formation
08:06
Implicit and Explicit Long-Term Memories